Kubelet
概述
参考:
更新时间:2022 年 2 月 23 日,Kubernetes 的源码目录随着更新迭代,也在不断变化中
目录结构
kubelet 代码分两部分,在 cmd/kubelet 和 pkg/kubelet 中
- cmd/kubelet/*
$ tree -L 2 -p cmd/kubelet
cmd/kubelet
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] BUILD
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] OWNERS
├── [drwxrwxrwx] app
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] BUILD
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] OWNERS
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] auth.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] init_others.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] init_windows.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] init_windows_test.go
│ ├── [drwxrwxrwx] options
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] plugins.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] plugins_providerless.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] plugins_providers.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] server.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] server_bootstrap_test.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] server_linux.go
│ ├── [-rwxrwxrwx] server_test.go
│ └── [-rwxrwxrwx] server_unsupported.go
└── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet.go
- pkg/kubelet/*
$ tree -L 1 -p pkg/kubelet
pkg/kubelet
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] BUILD
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] OWNERS
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] active_deadline.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] active_deadline_test.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] apis
├── [drwxrwxrwx] cadvisor
├── [drwxrwxrwx] certificate
├── [drwxrwxrwx] checkpointmanager
├── [drwxrwxrwx] client
├── [drwxrwxrwx] cloudresource
├── [drwxrwxrwx] cm
├── [drwxrwxrwx] config
├── [drwxrwxrwx] configmap
├── [drwxrwxrwx] container
├── [drwxrwxrwx] cri
├── [drwxrwxrwx] custommetrics
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] doc.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] dockershim
├── [drwxrwxrwx] envvars
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] errors.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] events
├── [drwxrwxrwx] eviction
├── [drwxrwxrwx] images
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_dockershim.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_dockershim_nodocker.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_getters.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_getters_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_network.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_network_linux.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_network_others.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_network_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_node_status.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_node_status_others.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_node_status_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_node_status_windows.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_pods.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_pods_linux_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_pods_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_pods_windows_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_resources.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_resources_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_volumes.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_volumes_linux_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] kubelet_volumes_test.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] kubeletconfig
├── [drwxrwxrwx] kuberuntime
├── [drwxrwxrwx] leaky
├── [drwxrwxrwx] legacy
├── [drwxrwxrwx] lifecycle
├── [drwxrwxrwx] logs
├── [drwxrwxrwx] metrics
├── [drwxrwxrwx] network
├── [drwxrwxrwx] nodelease
├── [drwxrwxrwx] nodestatus
├── [drwxrwxrwx] oom
├── [drwxrwxrwx] pleg
├── [drwxrwxrwx] pluginmanager
├── [drwxrwxrwx] pod
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] pod_container_deletor.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] pod_container_deletor_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] pod_workers.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] pod_workers_test.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] preemption
├── [drwxrwxrwx] prober
├── [drwxrwxrwx] qos
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] reason_cache.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] reason_cache_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] runonce.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] runonce_test.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] runtime.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] runtimeclass
├── [drwxrwxrwx] secret
├── [drwxrwxrwx] server
├── [drwxrwxrwx] stats
├── [drwxrwxrwx] status
├── [drwxrwxrwx] sysctl
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] time_cache.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] time_cache_test.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] token
├── [drwxrwxrwx] types
├── [drwxrwxrwx] util
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] util.go
├── [-rwxrwxrwx] volume_host.go
├── [drwxrwxrwx] volumemanager
└── [drwxrwxrwx] winstats
架构
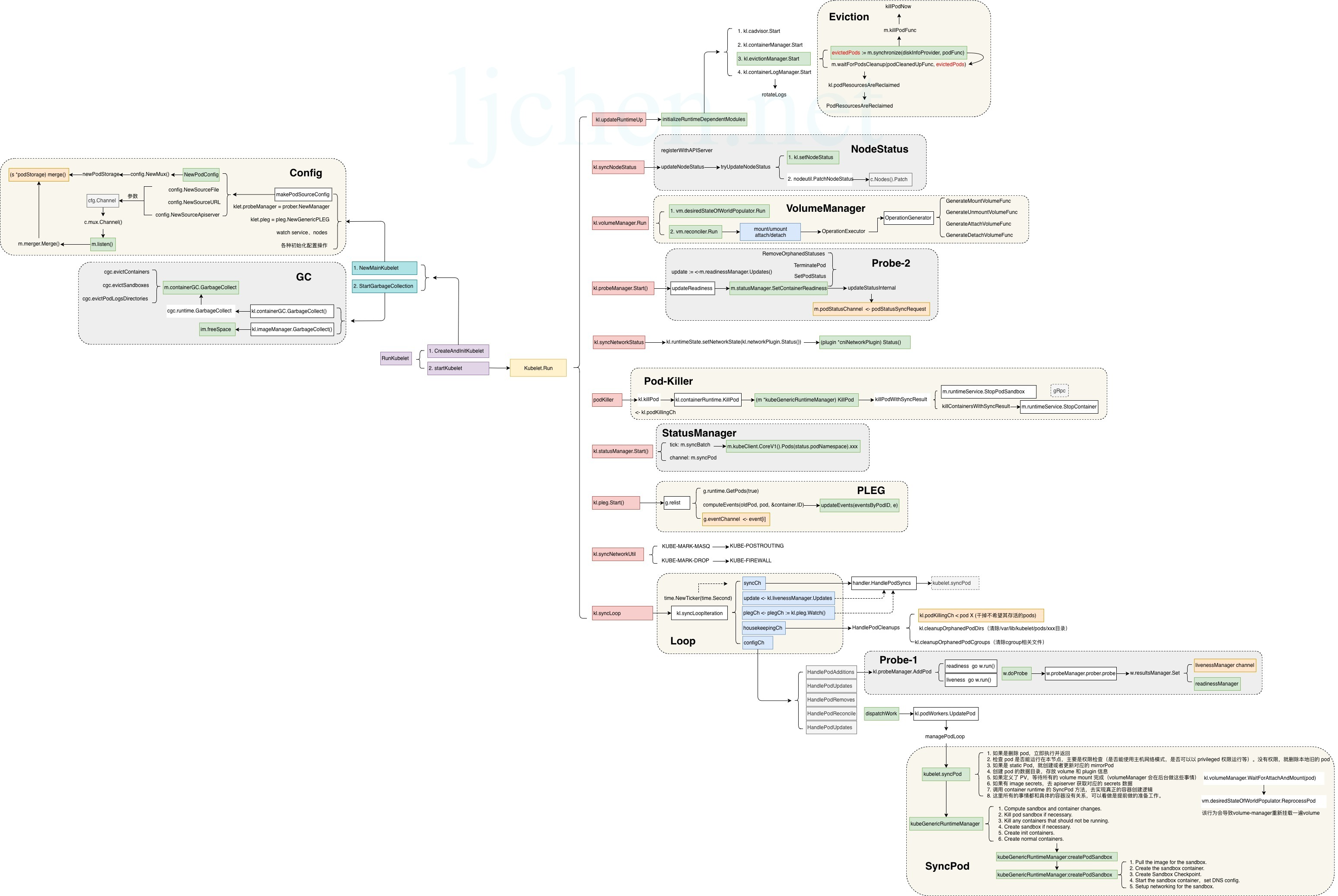
Kubelet 模块化
Kubelet 整体由多个模块组成,这些模块通过多个途径来初始化
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.gokubelet.initializeModules()# 初始化不需要容器运行时启动的内部模块。- 注意:这里的模块不能依赖于未在此处初始化的模块
kubelet.initialieRuntimeDependentModules()# 初始化需要容器运行时的内部模块
在 《[Kubelet 启动流程](/docs/10.云原生/2.3.Kubernetes%20 容器编排系统/Kubernetes%20 开发/源码解析/Kubelet%20 源码/Kubelet%20 启动流程.md 源码/Kubelet 启动流程.md)》章节中包含了初始化模块的执行逻辑
在 Kubelet 代码中,每个模块通常都放在 pkg/kubelet/ 目录下的某个单独的目录中。所有的模块通常都被包含在两个结构体中:
Kubelet{}# 代表 kubelet 内部跟 Pod 息息相关的模块,比如 podManager(pod 信息存储模块),probeManager(pod 测活模块)等等- 通常实例化成名为 klet 或 kl 的对象
Dependencies{}# 包含一些 kubelet 依赖的外部功能,比如 cadvisor(监控功能),containerManager(cgroup 管理功能)- 通常实例化成名为 kubeDeps 的对象
这些模块在代码中的表现形式是结构体,使用模块时,会将结构体实例化为“对象”,然后调用对象的方法。只不过为了便于扩展,都将这些结构体抽象为接口,所以 Kubelet{} 与 Dependencies{} 两个结构体中,其中很多属性的类型,通常都是接口,而这些模块结构体,都实现了对应的接口。
这些模块基于生产者/消费者的模型互相配合工作。整个 Kubelet 的工作模式将会围绕着不同的生产者生产出来的不同的有关 Pod 的消息来调用相应的消费者,以便完成不同的任务,比如 创建 Pod、删除 Pod 等等。
源码:pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go - kubelet.syncLoopIteration()
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(configCh <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler,
select {
case u, open := <-configCh:
case e := <-plegCh:
case <-syncCh:
case update := <-kl.livenessManager.Updates():
case update := <-kl.readinessManager.Updates():
case update := <-kl.startupManager.Updates():
case <-housekeepingCh:
}
}
从上面的代码中可以看到,Kubelet 主要包括 5 个生产者:
- configCh # 由 kubeDeps 对象中的 PodConfig 子模块提供,该模块将同时 watch 3 个不同来源的 pod 信息的变化(file,http,apiserver),一旦某个来源的 pod 信息发生了更新(创建/更新/删除),这个 channel 中就会出现被更新的 pod 信息和更新的具体操作。
- health manager # 由 3 个检查组成。用以同步失败的 Pod 或其中一个或多个健康检查失败的容器。
- liveness
- syncCh # 一个周期性的信号源(默认 1 秒),周期性同步所有需要再次同步的 pod。
- housekeepingCh # 一个周期性信号源(默认 2 秒),周期性的清理一些无用 pod。
- plegCh # 由 kubelet 对象中的 pleg 子模块提供,该模块主要用于周期性地向 container runtime 查询当前所有容器的状态,如果状态发生变化,则这个 channel 产生事件
上述生产者生产的消息都由 Kubelet{} 结构体实例化的对象统一接收,之后调用其他功能函数完成后续操作。比如 SyncHandler 接口下的所有函数:
type SyncHandler interface {
HandlePodAdditions(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodUpdates(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodRemoves(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodReconcile(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodSyncs(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodCleanups() error
}
每一个处理函数背后可能都需要 kubelet 对象去调用背后多个内部子模块来共同完成,比如 HandlePodAddition 函数,处理 Pod 的创建,其中可能需要
- 调用 kubelet.podManager 子模块 AddPod 函数,注册该 pod 信息
- 调用 kubelet.podWorker 子模块为这个 Pod 创建单独的 worker goroutine 完成具体的操作
- 调用 kubelet.containerManager 子模块为这个 Pod 创建相应的 Pod Level Cgroup
- 调用 kubelet.volumeManager 子模块为这个 Pod 准备需要被 Mount 到容器中的文件系统
- 调用 kubelet.containerRuntime 子模块真正的创建 Pod 的实体
- ….
所以综上,整个 Kubelet 的所有内部子模块就是通过这种生产者消费者模型协调工作,及时将 Pod 以用户期望的状态维护在它所在的机器上。
上面说到的只是 Kubelet 中和 Pod 管理相关的结构,kubelet 中还包括一些为了 维护物理机稳定性、同步更新物理机配置 等目的,周期性不间断工作的子模块,他们也是 Kubelet 中非常重要的一部分。
Kubelet 模块
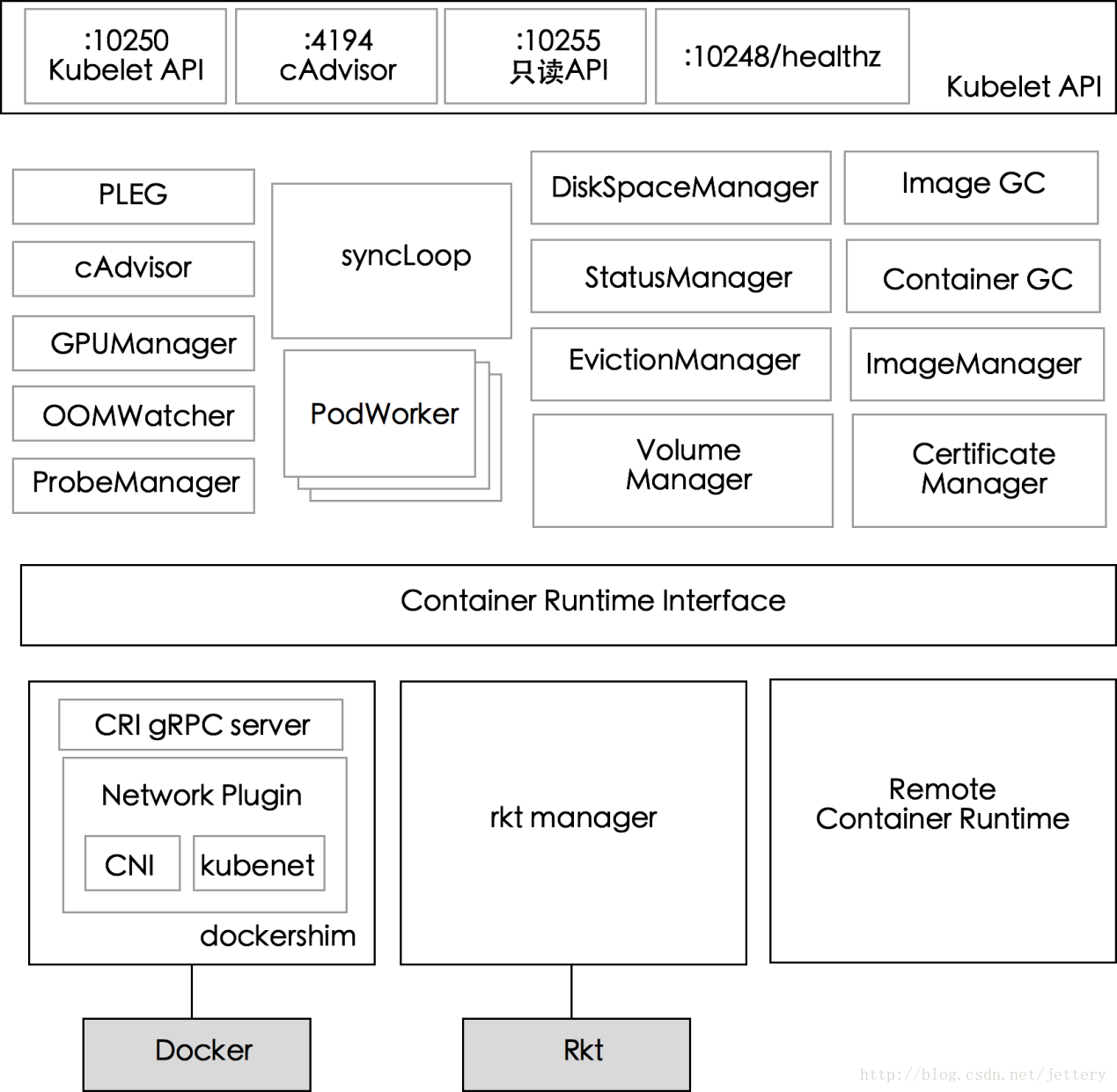 上图展示了 Kubelet 组件中的模块以及模块间的划分。
上图展示了 Kubelet 组件中的模块以及模块间的划分。
- PLEG(Pod Lifecycle Event Generator) PLEG 是 kubelet 的核心模块,PLEG 会一直调用 container runtime 获取本节点 containers/sandboxes 的信息,并与自身维护的 pods cache 信息进行对比,生成对应的 PodLifecycleEvent,然后输出到 eventChannel 中,通过 eventChannel 发送到 kubelet syncLoop 进行消费,然后由 kubelet syncPod 来触发 pod 同步处理过程,最终达到用户的期望状态。
- cAdvisor # (https://github.com/google/cadvisor)google 开发的容器监控工具,集成在 kubelet 中,起到收集本节点和容器的监控信息,大部分公司对容器的监控数据都是从 cAdvisor 中获取的 ,cAvisor 模块对外提供了 interface 接口,该接口也被 imageManager,OOMWatcher,containerManager 等所使用。
- 代码:
pkg/kubelet/cadvisor/cadvisor_linux.go。cadvisor 包中名为{}的结构体实现了本包中的{}接口
- 代码:
- OOMWatcher # 系统 OOM 的监听器,会与 cadvisor 模块之间建立 SystemOOM,通过 Watch 方式从 cadvisor 那里收到的 OOM 信号,并产生相关事件。
- 代码:
pkg/kubelet/oom/oom_watcher_linux.go。oom 包中名为realWatcher{}的结构体实现了本包中的Watcher{}接口
- 代码:
- probeManager probeManager 依赖于 statusManager,livenessManager,containerRefManager,会定时去监控 pod 中容器的健康状况,当前支持两种类型的探针:livenessProbe 和 readinessProbe。 livenessProbe:用于判断容器是否存活,如果探测失败,kubelet 会 kill 掉该容器,并根据容器的重启策略做相应的处理。 readinessProbe:用于判断容器是否启动完成,将探测成功的容器加入到该 pod 所在 service 的 endpoints 中,反之则移除。readinessProbe 和 livenessProbe 有三种实现方式:http、tcp 以及 cmd。
- statusManager statusManager 负责维护状态信息,并把 pod 状态更新到 apiserver,但是它并不负责监控 pod 状态的变化,而是提供对应的接口供其他组件调用,比如 probeManager。
- containerRefManager 容器引用的管理,相对简单的 Manager,用来报告容器的创建,失败等事件,通过定义 map 来实现了 containerID 与 v1.ObjectReferece 容器引用的映射。
- EvictionManager # 当节点的内存、磁盘或 inode 等资源不足时,达到了配置的 evict 策略, node 会变为 pressure 状态,此时 kubelet 会按照 qosClass 顺序来驱赶 pod,以此来保证节点的稳定性。可以通过配置 kubelet 启动参数 –eviction-hard= 来决定 evict 的策略值。
- 代码:
pkg/kubelet/eviction/eviction_manager.go。eviction 包中名为managerImpl{}的结构体实现了本包中的Manager{}接口。
- 代码:
- ImageGCManager # 负责 node 节点的镜像回收,当本地的存放镜像的本地磁盘空间达到某阈值的时候,会触发镜像的回收,删除掉不被 pod 所使用的镜像,回收镜像的阈值可以通过 kubelet 的启动参数 –image-gc-high-threshold 和 –image-gc-low-threshold 来设置。
- 代码:
pkg/kubelet/images/image_gc_manager.go。images 包中名为realImageGCManager{}的结构体实现了本包中的ImageGCManager{}接口
- 代码:
- containerGC containerGC 负责清理 node 节点上已消亡的 container,具体的 GC 操作由 runtime 来实现。~~
- imageManager 调用 kubecontainer 提供的 PullImage/GetImageRef/ListImages/RemoveImage/ImageStates 方法来保证 pod 运行所需要的镜像。
- volumeManager 负责 node 节点上 pod 所使用 volume 的管理,volume 与 pod 的生命周期关联,负责 pod 创建删除过程中 volume 的 mount/umount/attach/detach 流程,kubernetes 采用 volume Plugins 的方式,实现存储卷的挂载等操作,内置几十种存储插件。~~
- ContainerManager # 负责 node 节点上运行的容器的 cgroup 配置信息,kubelet 启动参数如果指定 –cgroups-per-qos 的时候,kubelet 会启动 goroutine 来周期性的更新 pod 的 cgroup 信息,维护其正确性,该参数默认为 true,实现了 pod 的 Guaranteed/BestEffort/Burstable 三种级别的 Qos。
- 代码:
pkg/kubelet/cm/container_manager_linux.go。cm 包中名为containerManagerImpl{}的结构体实现了本包中的ContainerManager{}接口
- 代码:
- runtimeManager containerRuntime 负责 kubelet 与不同的 runtime 实现进行对接,实现对于底层 container 的操作,初始化之后得到的 runtime 实例将会被之前描述的组件所使用。可以通过 kubelet 的启动参数 –container-runtime 来定义是使用 docker 还是 rkt,默认是 docker。
- podManager podManager 提供了接口来存储和访问 pod 的信息,维持 static pod 和 mirror pods 的关系,podManager 会被 statusManager/volumeManager/runtimeManager 所调用,podManager 的接口处理流程里面会调用 secretManager 以及 configMapManager。
在 v1.12 中,Kubelet 有 18 个 manager:
certificateManager
cgroupManager
containerManager
cpuManager
nodeContainerManager
configmapManager
containerReferenceManager
evictionManager
nvidiaGpuManager
imageGCManager
kuberuntimeManager
hostportManager
podManager
proberManager
secretManager
statusManager
volumeManager
tokenManager
结构体
KubeletServer 结构体
KubeletServer 结构体封装了启动 kubelet 所需的所有参数,这些可以通过 命令行 或 配置文件 设置。在调用各种运行 kubelet 的函数或方法的时候,通常都需要将该结构体作为参数。
源码:cmd/kubelet/app/options/options.go
type KubeletServer struct {
KubeletFlags
kubeletconfig.KubeletConfiguration
}
Kubelet 结构体
Kubelet 结构体是 kubelet 的主要实现,当 Kubelet 运行后调用的各种方法,都是该结构体的方法。该结构体实现了多个接口:
SyncHandler接口Bootstrap接口- …… 等
源码:pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
type Kubelet struct {
......
}
Kubelet 结构体中的属性
- kubeletConfiguration kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration
- // hostname is the hostname the kubelet detected or was given via flag/config
- hostname string
- // hostnameOverridden indicates the hostname was overridden via flag/config
- hostnameOverridden bool
- nodeName types.NodeName
- runtimeCache kubecontainer.RuntimeCache
- kubeClient clientset.Interface
- heartbeatClient clientset.Interface
- rootDirectory string
- lastObservedNodeAddressesMux sync.RWMutex
- lastObservedNodeAddresses []v1.NodeAddress
- // onRepeatedHeartbeatFailure is called when a heartbeat operation fails more than once. optional.
- onRepeatedHeartbeatFailure func()
- podWorkers PodWorkers # 响应事件处理同步 Pod.
- // resyncInterval is the interval between periodic full reconciliations of
- // pods on this node.
- resyncInterval time.Duration
- // sourcesReady records the sources seen by the kubelet, it is thread-safe.
- sourcesReady config.SourcesReady
- // podManager is a facade that abstracts away the various sources of pods
- // this Kubelet services.
- podManager kubepod.Manager
- evictionManager eviction.Manager # 驱逐管理器。一个模块。用于观察和应对可能影响节点稳定性的情况
- // Optional, defaults to /logs/ from /var/log
- logServer http.Handler
- // Optional, defaults to simple Docker implementation
- runner kubecontainer.CommandRunner
- // cAdvisor used for container information.
- cadvisor cadvisor.Interface
- // Set to true to have the node register itself with the apiserver.
- registerNode bool
- // List of taints to add to a node object when the kubelet registers itself.
- registerWithTaints []v1.Taint
- // Set to true to have the node register itself as schedulable.
- registerSchedulable bool
- // for internal book keeping; access only from within registerWithApiserver
- registrationCompleted bool
- // dnsConfigurer is used for setting up DNS resolver configuration when launching pods.
- dnsConfigurer *dns.Configurer
- // masterServiceNamespace is the namespace that the master service is exposed in.
- masterServiceNamespace string
- // serviceLister knows how to list services
- serviceLister serviceLister
- // serviceHasSynced indicates whether services have been sync’d at least once.
- // Check this before trusting a response from the lister.
- serviceHasSynced cache.InformerSynced
- // nodeLister knows how to list nodes
- nodeLister corelisters.NodeLister
- // nodeHasSynced indicates whether nodes have been sync’d at least once.
- // Check this before trusting a response from the node lister.
- nodeHasSynced cache.InformerSynced
- // a list of node labels to register
- nodeLabels map[string]string
- // Last timestamp when runtime responded on ping.
- // Mutex is used to protect this value.
- runtimeState *runtimeState
- // Volume plugins.
- volumePluginMgr *volume.VolumePluginMgr
- // Handles container probing.
- probeManager prober.Manager
- // Manages container health check results.
- livenessManager proberesults.Manager
- readinessManager proberesults.Manager
- startupManager proberesults.Manager
- // How long to keep idle streaming command execution/port forwarding
- // connections open before terminating them
- streamingConnectionIdleTimeout time.Duration
- // The EventRecorder to use
- recorder record.EventRecorder
- // Policy for handling garbage collection of dead containers.
- containerGC kubecontainer.GC
- // Manager for image garbage collection.
- imageManager images.ImageGCManager
- // Manager for container logs.
- containerLogManager logs.ContainerLogManager
- // Secret manager.
- secretManager secret.Manager
- // ConfigMap manager.
- configMapManager configmap.Manager
- // Cached MachineInfo returned by cadvisor.
- machineInfoLock sync.RWMutex
- machineInfo *cadvisorapi.MachineInfo
- // Handles certificate rotations.
- serverCertificateManager certificate.Manager
- // Syncs pods statuses with apiserver; also used as a cache of statuses.
- statusManager status.Manager
- // VolumeManager runs a set of asynchronous loops that figure out which
- // volumes need to be attached/mounted/unmounted/detached based on the pods
- // scheduled on this node and makes it so.
- volumeManager volumemanager.VolumeManager
- // Cloud provider interface.
- cloud cloudprovider.Interface
- // Handles requests to cloud provider with timeout
- cloudResourceSyncManager cloudresource.SyncManager
- // Indicates that the node initialization happens in an external cloud controller
- externalCloudProvider bool
- // Reference to this node.
- nodeRef *v1.ObjectReference
- // Container runtime.
- containerRuntime kubecontainer.Runtime
- // Streaming runtime handles container streaming.
- streamingRuntime kubecontainer.StreamingRuntime
- // Container runtime service (needed by container runtime Start()).
- runtimeService internalapi.RuntimeService
- // reasonCache caches the failure reason of the last creation of all containers, which is
- // used for generating ContainerStatus.
- reasonCache *ReasonCache
- // nodeStatusUpdateFrequency specifies how often kubelet computes node status. If node lease
- // feature is not enabled, it is also the frequency that kubelet posts node status to master.
- // In that case, be cautious when changing the constant, it must work with nodeMonitorGracePeriod
- // in nodecontroller. There are several constraints:
- // 1. nodeMonitorGracePeriod must be N times more than nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, where
- // N means number of retries allowed for kubelet to post node status. It is pointless
- // to make nodeMonitorGracePeriod be less than nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, since there
- // will only be fresh values from Kubelet at an interval of nodeStatusUpdateFrequency.
- // The constant must be less than podEvictionTimeout.
- // 2. nodeStatusUpdateFrequency needs to be large enough for kubelet to generate node
- // status. Kubelet may fail to update node status reliably if the value is too small,
- // as it takes time to gather all necessary node information.
- nodeStatusUpdateFrequency time.Duration
- // nodeStatusReportFrequency is the frequency that kubelet posts node
- // status to master. It is only used when node lease feature is enabled.
- nodeStatusReportFrequency time.Duration
- // lastStatusReportTime is the time when node status was last reported.
- lastStatusReportTime time.Time
- // lastContainerStartedTime is the time of the last ContainerStarted event observed per pod
- lastContainerStartedTime *timeCache
- // syncNodeStatusMux is a lock on updating the node status, because this path is not thread-safe.
- // This lock is used by Kubelet.syncNodeStatus function and shouldn’t be used anywhere else.
- syncNodeStatusMux sync.Mutex
- // updatePodCIDRMux is a lock on updating pod CIDR, because this path is not thread-safe.
- // This lock is used by Kubelet.syncNodeStatus function and shouldn’t be used anywhere else.
- updatePodCIDRMux sync.Mutex
- // updateRuntimeMux is a lock on updating runtime, because this path is not thread-safe.
- // This lock is used by Kubelet.updateRuntimeUp function and shouldn’t be used anywhere else.
- updateRuntimeMux sync.Mutex
- // nodeLeaseController claims and renews the node lease for this Kubelet
- nodeLeaseController lease.Controller
- // Generates pod events.
- pleg pleg.PodLifecycleEventGenerator
- // Store kubecontainer.PodStatus for all pods.
- podCache kubecontainer.Cache
- // os is a facade for various syscalls that need to be mocked during testing.
- os kubecontainer.OSInterface
- // Watcher of out of memory events.
- oomWatcher oomwatcher.Watcher
- // Monitor resource usage
- resourceAnalyzer serverstats.ResourceAnalyzer
- // Whether or not we should have the QOS cgroup hierarchy for resource management
- cgroupsPerQOS bool
- // If non-empty, pass this to the container runtime as the root cgroup.
- cgroupRoot string
- // Mounter to use for volumes.
- mounter mount.Interface
- // hostutil to interact with filesystems
- hostutil hostutil.HostUtils
- // subpather to execute subpath actions
- subpather subpath.Interface
- // Manager of non-Runtime containers.
- containerManager cm.ContainerManager
- // Maximum Number of Pods which can be run by this Kubelet
- maxPods int
- // Monitor Kubelet’s sync loop
- syncLoopMonitor atomic.Value
- // Container restart Backoff
- backOff *flowcontrol.Backoff
- // Information about the ports which are opened by daemons on Node running this Kubelet server.
- daemonEndpoints *v1.NodeDaemonEndpoints
- // A queue used to trigger pod workers.
- workQueue queue.WorkQueue
- // oneTimeInitializer is used to initialize modules that are dependent on the runtime to be up.
- oneTimeInitializer sync.Once
- // If set, use this IP address or addresses for the node
- nodeIPs []net.IP
- // use this function to validate the kubelet nodeIP
- nodeIPValidator func(net.IP) error
- // If non-nil, this is a unique identifier for the node in an external database, eg. cloudprovider
- providerID string
- // clock is an interface that provides time related functionality in a way that makes it
- // easy to test the code.
- clock clock.WithTicker
- // handlers called during the tryUpdateNodeStatus cycle
- setNodeStatusFuncs []func(*v1.Node) error
- lastNodeUnschedulableLock sync.Mutex
- // maintains Node.Spec.Unschedulable value from previous run of tryUpdateNodeStatus()
- lastNodeUnschedulable bool
- // the list of handlers to call during pod admission.
- admitHandlers lifecycle.PodAdmitHandlers
- // softAdmithandlers are applied to the pod after it is admitted by the Kubelet, but before it is
- // run. A pod rejected by a softAdmitHandler will be left in a Pending state indefinitely. If a
- // rejected pod should not be recreated, or the scheduler is not aware of the rejection rule, the
- // admission rule should be applied by a softAdmitHandler.
- softAdmitHandlers lifecycle.PodAdmitHandlers
- // the list of handlers to call during pod sync loop.
- lifecycle.PodSyncLoopHandlers
- // the list of handlers to call during pod sync.
- lifecycle.PodSyncHandlers
- // the number of allowed pods per core
- podsPerCore int
- // enableControllerAttachDetach indicates the Attach/Detach controller
- // should manage attachment/detachment of volumes scheduled to this node,
- // and disable kubelet from executing any attach/detach operations
- enableControllerAttachDetach bool
- // trigger deleting containers in a pod
- containerDeletor *podContainerDeletor
- // config iptables util rules
- makeIPTablesUtilChains bool
- // The bit of the fwmark space to mark packets for SNAT.
- iptablesMasqueradeBit int
- // The bit of the fwmark space to mark packets for dropping.
- iptablesDropBit int
- // The AppArmor validator for checking whether AppArmor is supported.
- appArmorValidator apparmor.Validator
- // experimentalHostUserNamespaceDefaulting sets userns=true when users request host namespaces (pid, ipc, net),
- // are using non-namespaced capabilities (mknod, sys_time, sys_module), the pod contains a privileged container,
- // or using host path volumes.
- // This should only be enabled when the container runtime is performing user remapping AND if the
- // experimental behavior is desired.
- experimentalHostUserNamespaceDefaulting bool
- // StatsProvider provides the node and the container stats.
- StatsProvider *stats.Provider
- // This flag, if set, instructs the kubelet to keep volumes from terminated pods mounted to the node.
- // This can be useful for debugging volume related issues.
- keepTerminatedPodVolumes bool// DEPRECATED
- // pluginmanager runs a set of asynchronous loops that figure out which
- // plugins need to be registered/unregistered based on this node and makes it so.
- pluginManager pluginmanager.PluginManager
- // This flag sets a maximum number of images to report in the node status.
- nodeStatusMaxImages int32
- // Handles RuntimeClass objects for the Kubelet.
- runtimeClassManager *runtimeclass.Manager
- // Handles node shutdown events for the Node.
- shutdownManager nodeshutdown.Manager
Dependencies 结构体
源码:pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
podWorkers 结构体
podWorkers struct{} 实现了如下接口
[PodWorkers interface{}](#Kg8vN),该接口被包含在kubelet struct{}中
源码:pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go
kubeGenericRuntimeManager 结构体
该结构体实现了如下接口
Runtime interface{}
源码:pkg/kubelet/kuberuntime/kuberuntime_manager.go-type kubeGenericRuntimeManager struct{}
type kubeGenericRuntimeManager struct {
}
结构体属性
runtimeName string recorder record.EventRecorder osInterface kubecontainer.OSInterface // machineInfo contains the machine information. machineInfo cadvisorapi.MachineInfo // Container GC manager containerGCcontainerGC // Keyring for pulling images keyring credentialprovider.DockerKeyring // Runner of lifecycle events. runner kubecontainer.HandlerRunner // RuntimeHelper that wraps kubelet to generate runtime container options. runtimeHelper kubecontainer.RuntimeHelper // Health check results. livenessManager proberesults.Manager readinessManager proberesults.Manager startupManager proberesults.Manager // If true, enforce container cpu limits with CFS quota support cpuCFSQuota bool // CPUCFSQuotaPeriod sets the CPU CFS quota period value, cpu.cfs_period_us, defaults to 100ms cpuCFSQuotaPeriod metav1.Duration // wrapped image puller. imagePuller images.ImageManager runtimeService internalapi.RuntimeService # gRPC 服务客户端,即 CRI,通常由第三方容器工具实现该接口,比如 Containerd imageService internalapi.ImageManagerService // The version cache of runtime daemon. versionCache cache.ObjectCache // The directory path for seccomp profiles. seccompProfileRoot string // Internal lifecycle event handlers for container resource management. internalLifecycle cm.InternalContainerLifecycle // Manage container logs. logManager logs.ContainerLogManager // Manage RuntimeClass resources. runtimeClassManagerruntimeclass.Manager // Cache last per-container error message to reduce log spam logReduction *logreduction.LogReduction // PodState provider instance podStateProvider podStateProvider // Use RuntimeDefault as the default seccomp profile for all workloads. seccompDefault bool // MemorySwapBehavior defines how swap is used memorySwapBehavior string //Function to get node allocatable resources getNodeAllocatable func() v1.ResourceList // Memory throttling factor for MemoryQoS memoryThrottlingFactor float64
接口
Bootstrap 接口
Bootstrap 接口中包含了在引导 kubelet 启动并运行时所需要的各种行为,针对初始化协议
源码:pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
type Bootstrap interface {
GetConfiguration() kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration
BirthCry()
StartGarbageCollection()
ListenAndServe(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, tlsOptions *server.TLSOptions, auth server.AuthInterface)
ListenAndServeReadOnly(address net.IP, port uint)
ListenAndServePodResources()
Run(-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate)
RunOnce(-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate) ([]RunPodResult, error)
}
SyncHandler 接口
SyncHandler 接口中包含了可以对 Pod 的各种处理,已被 kubelet 结构体实现,用在 syncLoop 中。这个接口中的方法,基本都是在 Bootstrap 接口中的 Run() 方法中调用的。
源码:pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
type SyncHandler interface {
HandlePodAdditions(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodUpdates(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodRemoves(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodReconcile(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodSyncs(pods []*v1.Pod)
HandlePodCleanups() error
}
PodWorkers 接口
详见《[PodWorker 模块](/docs/10.云原生/2.3.Kubernetes%20 容器编排系统/Kubernetes%20 开发/源码解析/Kubelet%20 源码/PodWorker%20 模块.md 源码/PodWorker 模块.md)》,PodWorkders 用于处理 Pod
Runtime 接口
Runtime interface{} 定义了容器 Runtime 应该实现的方法。该接口的实现必须是线程安全的。
源码:pkg/kubelet/container/runtime.go-type Runtime interface{}
type Runtime interface {
}
接口内的方法
Type() string # 返回容器运行时的类型 Version() (Version, error) # 返回容器运行时的版本信息 // APIVersion returns the cached API version information of the container // runtime. Implementation is expected to update this cache periodically. // This may be different from the runtime engine’s version. // TODO(random-liu): We should fold this into Version() APIVersion() (Version, error) // Status returns the status of the runtime. An error is returned if the Status // function itself fails, nil otherwise. Status() (*RuntimeStatus, error) // GetPods returns a list of containers grouped by pods. The boolean parameter // specifies whether the runtime returns all containers including those already // exited and dead containers (used for garbage collection). GetPods(all bool) ([]*Pod, error) // GarbageCollect removes dead containers using the specified container gc policy // If allSourcesReady is not true, it means that kubelet doesn’t have the // complete list of pods from all available sources (e.g., apiserver, http, // file). In this case, garbage collector should refrain itself from aggressive // behavior such as removing all containers of unrecognized pods (yet). // If evictNonDeletedPods is set to true, containers and sandboxes belonging to pods // that are terminated, but not deleted will be evicted. Otherwise, only deleted pods // will be GC’d. // TODO: Revisit this method and make it cleaner. GarbageCollect(gcPolicy GCPolicy, allSourcesReady bool, evictNonDeletedPods bool) error // SyncPod syncs the running pod into the desired pod. SyncPod(pod v1.Pod, podStatusPodStatus, pullSecrets []v1.Secret, backOff flowcontrol.Backoff) PodSyncResult // KillPod kills all the containers of a pod. Pod may be nil, running pod must not be. // TODO(random-liu): Return PodSyncResult in KillPod. // gracePeriodOverride if specified allows the caller to override the pod default grace period. // only hard kill paths are allowed to specify a gracePeriodOverride in the kubelet in order to not corrupt user data. // it is useful when doing SIGKILL for hard eviction scenarios, or max grace period during soft eviction scenarios. KillPod(podv1.Pod, runningPod Pod, gracePeriodOverride *int64) error // GetPodStatus retrieves the status of the pod, including the // information of all containers in the pod that are visible in Runtime. GetPodStatus(uid types.UID, name, namespace string) (*PodStatus, error) // TODO(vmarmol): Unify pod and containerID args. // GetContainerLogs returns logs of a specific container. By // default, it returns a snapshot of the container log. Set ‘follow’ to true to // stream the log. Set ‘follow’ to false and specify the number of lines (e.g. // “100” or “all”) to tail the log. GetContainerLogs(ctx context.Context, pod v1.Pod, containerID ContainerID, logOptionsv1.PodLogOptions, stdout, stderr io.Writer) (err error) // DeleteContainer deletes a container. If the container is still running, an error is returned. DeleteContainer(containerID ContainerID) error // ImageService provides methods to image-related methods. ImageService // UpdatePodCIDR sends a new podCIDR to the runtime. // This method just proxies a new runtimeConfig with the updated // CIDR value down to the runtime shim. UpdatePodCIDR(podCIDR string) error
CRI
在 kubernetes/cri-api 项目的 pkg/apis/services.go 中,有一个 RuntimeService interface{} 就是用来对接 CRI 的,这个接口应该由对应的容器运行时实现,同样,接口中的所有方法都必须是线程安全的。
我们在 Containerd 的代码中,这个 integration/remote/remote_runtime.go -RuntimeService struct{}就是实现了 CRI 的结构体
在 Kubelet 的代码中,RuntimeService Interface{} 被多个地方使用
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go-Dependencies.RemoeRuntimeServicepkg/kubelet/kuberuntime/kuberuntime_manager.go-kubeGenericRuntimeManager.runtimeService- 等等……
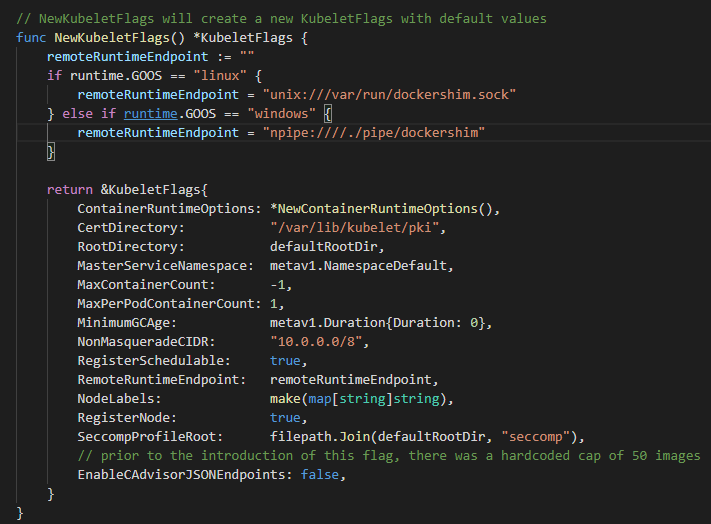
这个结构体中的属性,通常都是由 --container-runtime-endpoint 标志设置的,并在 PreInitRuntimeService() 函数中将指定的 CRI 赋值给 Dependencies.RemoteRuntimeService,以供后续使用。
这是 1.19 版本的
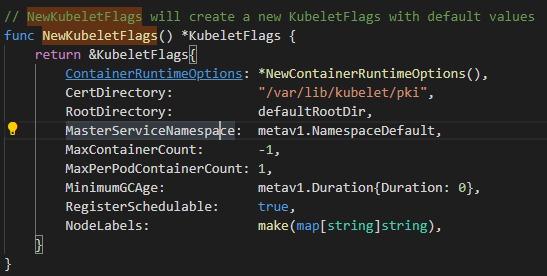
 这是 1.24 版本的
这是 1.24 版本的
反馈
此页是否对你有帮助?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.