Ansible Modules
概述
参考:
Modules(模块) 也被称为 Task Plugins(任务插件) 或 Library Plugins(插件库),Modules 是可以从 Ansible 的命令行或 Playbook 的任务中使用的代码块。Ansible 通常在受管理节点上执行每个模块以完成任务,并收集返回值。
注意:在 Ansible 2.10 及以上的版本中,大多数模块都被托管到 Collection(集合) 中。
我们可以通过命令行使用模块执行任务,比如
ansible webservers -m service -a "name=httpd state=started"
ansible webservers -m ping
ansible webservers -m command -a "/sbin/reboot -t now"
也可以在 Playbooks 中使用模块执行任务,比如
- name: restart webserver
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
等效于
ansible webservers -m service -a "name=httpd state=started"
每个模块都可以接受参数,以空格分割的 KEY=VALUE 格式。
注意:在命令行中使用模块与在 Playbooks 中使用模块时,可以传递的参数不太一样,比如 command 或 shell 模块,只需要传递需要运行的命令这个参数即可,但是在 Playbooks 中使用这两个模块,还可以传递其他参数。
所有模块执行完成后,都会有返回一个 JSON 格式的数据,这意味着可以使用任何编程语言编写模块。模块应该是幂等的,如果检测到当前状态与所需要的最终状态匹配,则应该避免再进行任何更改。
下面我们拿一个最简单的模块举例,ansible.builtin.command 模块,当我们使用 command 模块时,可以为其传递参数,在其执行完任务之后,还会有返回值。
简单示例
假如现在有这么一个 Playbooks
- name: test
command: whoami
register: info
- name: debug
debug:
msg: "{{info}}"
这个 Playbooks 的意思就是在受管理节点上执行 whoami 命令,并将返回值保存到 info 变量中,通过 debug 模块,将 info 变量中的内容输出出来,效果如下:
~/projects/DesistDaydream/ehualu/ansible/playbook]$ ansible-playbook 90-test.yaml
PLAY [test] *******************************************************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [90-test : test] *********************************************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [hw-cloud-xngy-jump-server-linux-2]
TASK [90-test : debug] ********************************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [hw-cloud-xngy-jump-server-linux-2] => {
"info": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"changed": true,
"cmd": [
"whoami"
],
"delta": "0:00:00.002447",
"end": "2021-10-09 23:05:10.491190",
"failed": false,
"rc": 0,
"start": "2021-10-09 23:05:10.488743",
"stderr": "",
"stderr_lines": [],
"stdout": "root",
"stdout_lines": [
"root"
]
}
}
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************************************************************************************************************
hw-cloud-xngy-jump-server-linux-2 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
我们对比官方文档中 command 模块的返回值,可以看到,与文档中的返回值保持一致。
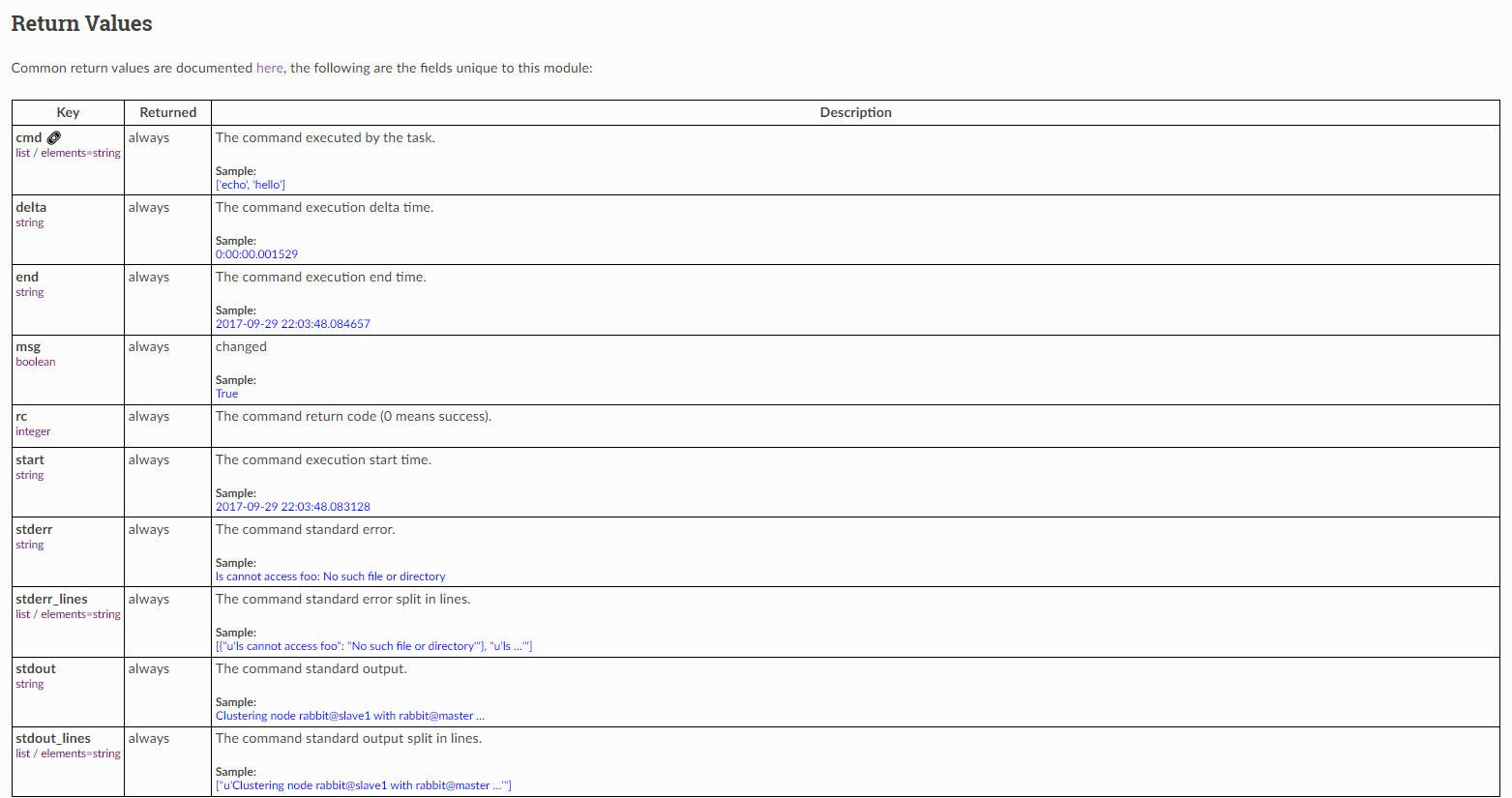
总结
所以,这也是为什么将 Moduels 称为代码的原因,所谓的 Modules,本质上就是代码写出来的程序,就像 Functions,具有形参,可以接受实参,执行完成后,还会有返回值。Ansible 通过模块执行完一个任务之后,就会处理这些返回值,将其 或保存、或展示、或丢弃 等等。同时,在 Playbooks 中,还可以通过判断语句,根据返回值的内容,决定下一个任务的运行模式。
我们可以通过 ansible-doc -l 命令查看所有可用的模块,或者从官方文档-Collections 文档中查看所有模块
还可以使用 ansible-doc MODULE 命令查看指定模块的文档
模块分类
参考:
在 2.10 版本之前,模块的分类非常清晰;2.10 版本之后,由于模块被合并到集合中,所以很多已经分类的模块被合并到 builtin(内置) 模块这个类别中,在这里则不再进行细致划分,非常乱。。。。
模块的保存位置(ansible python module location)也产生了变化:
~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.9.6
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = ['/home/desistdaydream/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 3.8.10 (default, Jun 22 2022, 20:18:18) [GCC 9.4.0]

~]# ansible --version
ansible [core 2.13.6]
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = ['/root/.ansible/plugins/modules', '/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules']
ansible python module location = /root/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/ansible
ansible collection location = /root/.ansible/collections:/usr/share/ansible/collections
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 3.8.10 (default, Jun 22 2022, 20:18:18) [GCC 9.4.0]
jinja version = 3.1.2
libyaml = True

反馈
此页是否对你有帮助?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.